October 14th, 2018 •
Comments Off on The Most Common Causes Of Fatigue

There are numerous potential causes of fatigue as a major complaint. They range from those that cause poor blood supply to the body’s tissues to illnesses that affect metabolism. From infections and inflammatory diseases to those that cause sleep disturbances.
Fatigue is also a common side effect of many medications. While numerous patients with psychological conditions often complain of fatigue (physical and mental), there are also a group of patients where unfortunately the cause of fatigue is never diagnosed. Read on to learn more about the most common causes of fatigue!

1.Metabolic Endocrine
Adrenal fatigue
Adrenal fatigue is a collection of signs and symptoms that is triggered when the adrenal glands function under their optimal level. As a result the body is unable to produce adequate amounts of hormones that are needed for it to function properly. The most telling symptom of adrenal fatigue is as the name already implies, “fatigue”. Other symptoms include an inability to handle stress, a weakened immune system, low blood sugar, and cravings for salty foods.
Anemia
Anemia refers to health conditions in which there is a decrease in the total amount of red blood cells. This can happen in instances where there is blood loss, the body does not produce enough red blood cells, or there are high rates of blood cell destruction. As a result the body does not receive enough oxygen rich blood and a person may feel weak or tired. Other sypmtoms that are linked to anemia are dizziness, headaches or shortness of breath.
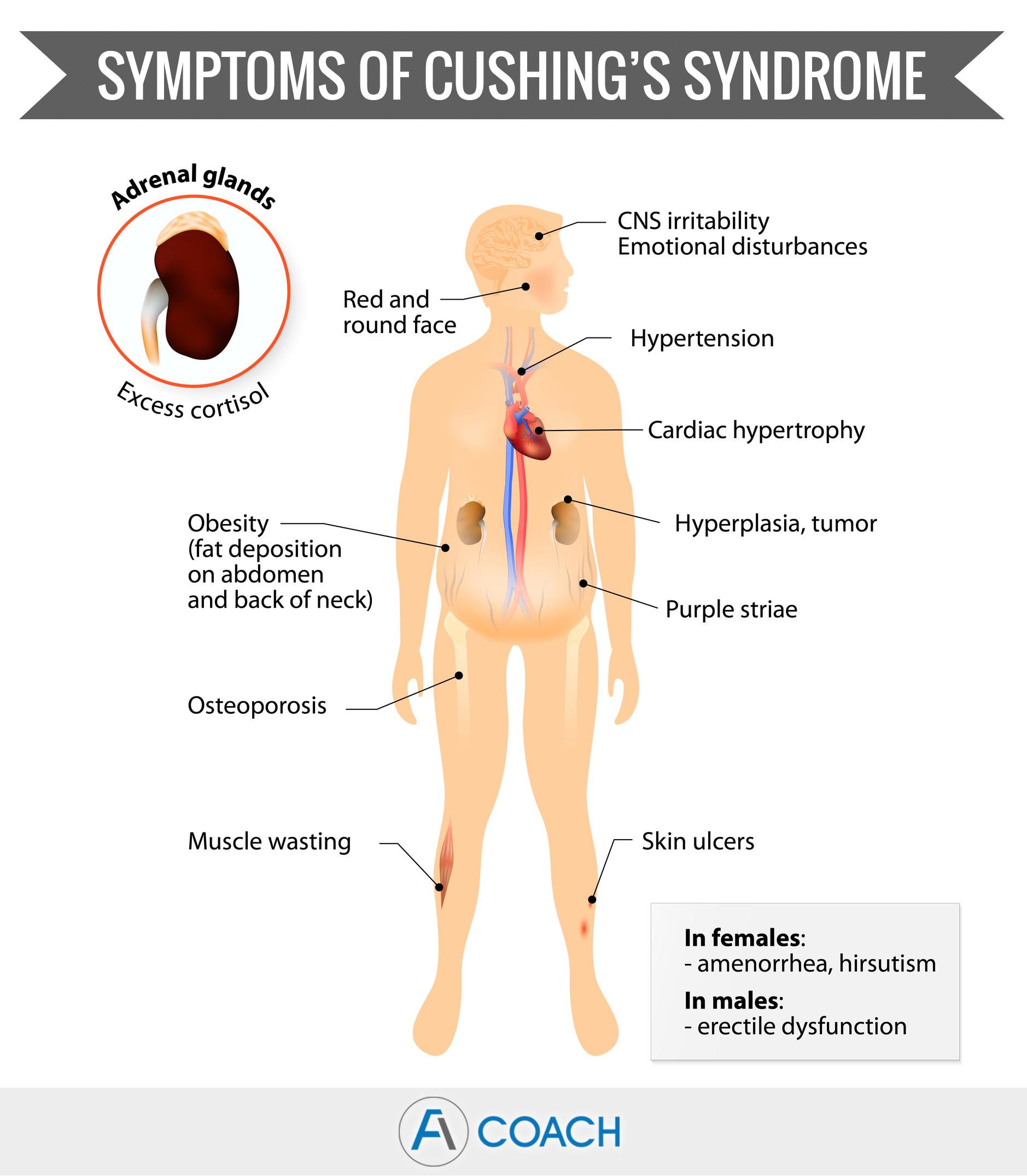
Cushing’s disease
Cushing’s Disease is a condition in which an excess of cortisol is produced indirectly by a pituitary tumor. If, over a long period of time, the body produces too much cortisol, it can lead to weight gain, insomnia, muscle and joint pain, premature aging, trigger emotional problems and making a patient feel constantly tired and weak. Cushing disease is a form of Cushing syndrome.
Diabetes
Diabetes is a disease where the amount of glucose (sugar) in the blood is consistently too high. Insulin is a hormone that is made by the pancreas and helps to move glucose that comes from food into the cells so that it can be used for energy. Sometimes the body is not able to make enough insulin or it can’t use the insulin well and the glucose stays in the blood. Over time too much glucose in the blood can cause health problems such as heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, nerve damage and eye problems.
People with diabetes can experience feeling fatigued because of the following factors:
- High blood sugar levels, from either the shortage of insulin or insulin resistance can interfere with the body´s ability to get glucose from the blood into the cells to meet the body´s energy demands.
- Also people that are on strong medication for diabetes and use insulin can feel fatigued because of low blood glucose levels.
Electrolyte abnormalities
Electrolytes are minerals like sodium, calcium, magnesium, potassium, chloride, phosphate, bicarbonate—that dissolve in the body’s fluids, creating electrically charged ions. They are crucial for helping the body with nerve and muscle function as well balancing body fluid levels. People with an electrolyte imbalance may experience fatigue, weakness, muscle spasm, twitching, convulsions, irregular heartbeat, confusion, blood pressure changes, nervous system or bone disorders.
There are many causes for an electrolyte imbalance such as:
- Loss of body fluids from prolonged sweating, vomiting, diarrhea, or high fever
- Poor diet
- Malabsorption
- Hormonal or endocrine disorders
- Kidney disease
- Certain medications
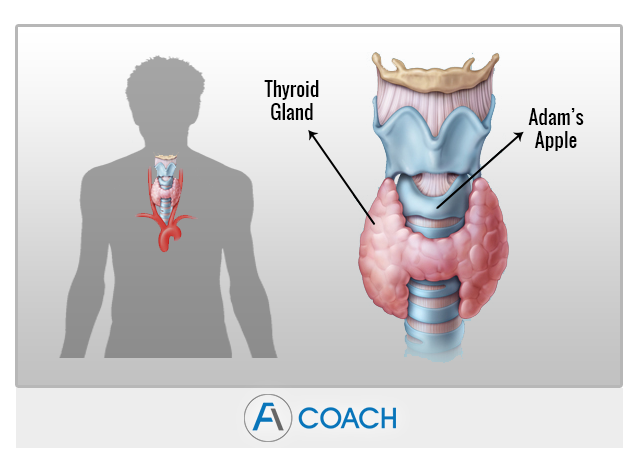
Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism, also known as low thyroid or underactive thyroid, is an endocrine disorder that occurs when the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormone. As a result the body’s processes start to slow down. As the processes slow down people start to feel cold, they tire more easily, they experience dry skin and hair loss.
Globally the most common cause of hypothyroidism is too little iodine in the diet. In the U.S. and other countries with sufficient iodine in the diet, the most common cause of hypothyroidism is autoimmune thyroid disease ( also known as Hashimoto’s disease), where the thyroid becomes inflamed and unable to produce adequate amounts of thyroid hormone. Other causes are radiation treatment and surgical removal of the thyroid.
Kidney disease
Chronic kidney disease, or chronic kidney failure, is a condition that involves the gradual loss of kidney function. Your kidneys remove waste products and excess fluids from your blood, which are then excreted in your urine. Signs and symptoms of chronic kidney disease include: sleep problems, nausea, vomiting, fatigue and weakness, changes in how you urinate, swelling of feet and ankles, chest pain, loss of appetite, muscle twitches and cramps, shortness of breath and hypertension.
Liver disease
Liver Disease, or Hepatitis, indicates inflammation and damage to liver cells. This damage can occur because of alcohol, drugs, toxins, viruses and inherited diseases. The most common symptoms include excessive tiredness, fatigue and lack of drive. Other more prominent symptoms are yellowing of the eyes, pale or light colored bowel movements and dark urine.
2.Infectious
Cytomegalovirus
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) is a virus that falls in the herpes family. CMV is passed through bodily fluids such as saliva and urine, semen, blood, tears, breastmilk and vaginal fluids. It can also be passed through blood transfusions and organ transplants. Most cases of CMV don’t cause symptoms. If people do experience symptoms, they often include fatigue, fever, swollen glands and sore throat.
Infectious mononucleosis
Infectious mononucleosis also known as glandular fever, is caused by the Epstein–Barr virus (EBV). It is one of the most common viruses to infect humans worldwide and it is spread through direct contact with bodily fluids of a person that is infected (such as saliva and blood). Most people are infected by the virus as children, when the disease produces no or but a few symptoms. In young adults, the disease often results in high fever, swollen lymph glands, a sore throat, and tiredness.the majority of the people get better on their own in 2 to 4 weeks; but feeling tired could last for months
Influenza (flu)
Fluenza, or more commonly called “the flu”, is a virus that attacks your respiratory system, your lungs, nose and throat. Initially the flu may feel like a common cold, with sneezing, a sore throat and a runny nose. But whereas colds develop slowly, the flu usually comes on suddenly. People also feel much worse with the flu. Symptoms of the flu are a high temperature, headache, cold sweats/shivers, aching joints and limbs and fatigue.
Hepatitis
Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. In most cases it’s caused by a virus. But it may also be caused by drugs, alcohol use, or certain medical conditions. The most common types are hepatitis A, B, and C. In the first weeks after infection sometimes there are no symptoms. When symptoms do happen people experience nausea, fatigue, belly pain, poor appetite, a mild fever or yellow skin. When hepatitis B and C become chronic they can lead to liver damage.
HIV infection
HIV is a chronic infection that targets the immune system. People with HIV may use up a lot of energy as they are continually trying to fight off the virus. But fatigue can also be indirectly linked to the HIV infection. These indirect causes of HIV fatigue can be insomnia, depression or HIV drug side effects.
Malaria
Malaria is a life-threatening tropical disease caused by parasites. It is transmitted to people through the bites of infected mosquitos. Malaria symptoms include fiver, flu-like symptoms, fatigue, body aches, chills, diarrhea vomiting and jaundice. Although malaria can be life-threatening, it can be treated with medication. The type of medication depends on where you were infected and which kind of malaria you have.
Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is a is a highly infectious disease that primarily affects the lungs. It is caused by bacteria that are spread through the air from person to person. If not treated properly, TB disease can be fatal. TB bacteria most commonly grow in the lungs, and can cause symptoms such as pain the chest, a bad cough or coughing up blood or sputum. Other symptoms include fever, unexplained fatigue, appetite loss, night sweats and weight loss. TB disease can be treated by medication.
3.Cardiac (heart) and Pulmonary (lungs)
Arrythmias
An arrhythmia is an irregular heartbeat. It means that the heart beats too quickly, too slowly, or with an irregular pattern. Symptoms of arrhythmias include pounding in the chest, palpitations, dizziness or feeling light-headed, chest discomfort, fainting, shortness of breath, weakness or fatigue. Many factors can affect the heart’s rhythm, such as smoking, congenital heart defects, stress and having had a heart attack. Some medicines or substances may also cause arrhythmias.
Asthma
Asthma is a common chronic inflammatory lung disease in which the airways narrow and swell. This makes breathing difficult and trigger wheezing, coughing and shortness of breath. Fatigue is an overlooked symptom of asthma. When oxygen levels are reduced the body doesn’t receive everything it needs to properly operate. Another reason for fatigue is that will people with asthma often don’t sleep well, because symptoms can become worse at night and flare up.
COPD
COPD, or Chronic obstructive lung disease, is a long-term, progressive lung disease that encompasses chronic bronchitis and emphysema. Some main symptoms of COPD are lack of energy, wheezing, chest tightness, blueness of the lips or fingernail beds, swelling in ankles or legs. COPD makes breathing difficult, which affects a person’s energy levels and can cause fatigue. This is because damaged lungs keep patients from having enough oxygen in their blood. People with COPD may also feel tired because they feel breathless.
Congestive heart failure
Congestive heart failure (CHF) is a progressive condition that occurs when the heart muscle is weakened and isn’t able to pump blood normally. It is often caused by other conditions that weaken the heart. Common symptoms include: bloating, fatigue, nausea, chest pain, shortness of breath and swelling in the legs and feet.
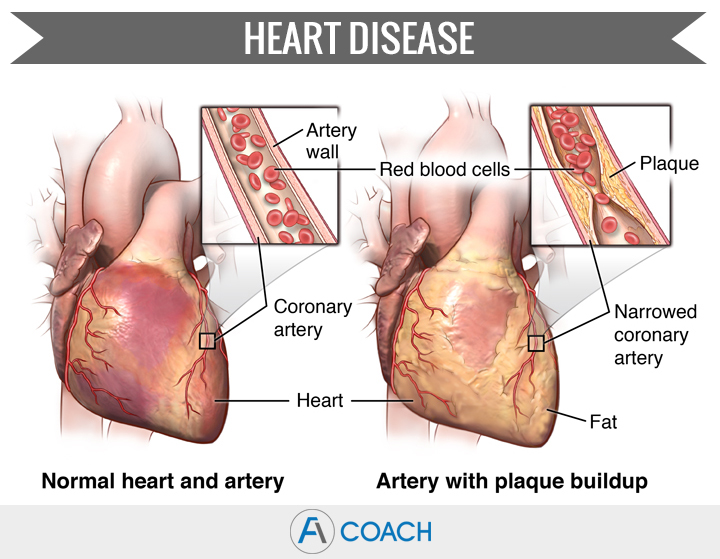
Coronary artery disease
Coronary artery disease (CAD), is a leading cause of death in men and women. It happens when the coronary arteries become narrow or blocked, typically caused by a build-up of cholesterol and fat in the blood that sticks to the inner walls of the arteries. CAD often does not cause symptoms until it becomes advanced. Subtle symptoms can include, indigestion-like sensations, dizziness, fatigue, and lack of energy. More noticeable symptoms of CAD include chest pain and shortness of breath.
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is an infection in one or both of the lungs that affects millions of people each year. It can be mild to life-threatening and is caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi . The most common symptoms include fever, cough, shaking chills, shortness of breath, headache, excessive sweating, loss of appetite, low energy and fatigue.
Valvular heart disease
Heart valve disease happens if one or more of the four heart valves don’t work well. This makes the heart work harder and affect its ability to pump blood. It occurs largely because of aging, but can also be the result of birth defects, infections and otger conditions that prevent the heart valves from fully opening or to let blood leak back into the heart chambers. The main sign of heart valve disease is an unusual heartbeat sound called a heart murmur. But the disease often worsens over time and can lead to other symptoms such as an unusual fatigue, swelling in feet, ankles, abdomen and veins in the neck.
4.Medications
Antihistamines
Antihistamines are medicines to treat symptoms of allergies, such as hay fever, dust, pet dander, hives, and reactions to insect bites or stings. Especially the older first-generation antihistamines caused a lot of drowsiness and fatigue and were also called sedating antihistamines. The newer antihistamines medicines fortunately cause less drowsiness and fatigue. It’s also good to note that tiredness itself is also a common allergy symptom.
Medication and drug withdrawal
Drug or medication withdrawal is a group of symptoms that happen after a person abruptly stops taking or suddenly decreases the intake of recreational drugs or medications. These withdrawal symptoms only occur after a person first has developed a form of dependence. This can be a psychological dependence or physical dependence or both.
Withdrawel symptoms are dose-dependent and also vary with the type of drug that is taken. Nicotine withdrawal can cause irritability, headache, insomnia, fatigue and difficulty concentrating. Withdrawel symptoms from opiates include sweating, anxiety, diarrhea and vomiting. Withdrawal symptoms from alcohol include shaking, irritability, fatigue, sweating and nausea.
Some antidepressants
Antidepressants are a group of medications used in the treatment of mental health problems and depression. They are some of the most commonly prescribed medications around and include: selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), atypical antidepressants, tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), and monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs).
Antidepressant medications offer a quick and simple method of relief from the pain and anguish of depression. They balance chemicals in the brain that affect emotions and mood. But like any medication, they come with side effects. The side effects vary depending on the drug but can include; sleepiness, diarrhea, insomnia, nausea or vomiting, headaches, dizziness, fatigue, blurred vision and high blood pressure.
Some blood pressure medications
Blood pressure medications are used for lowering the blood pressure inside your blood vessels, so that your heart does not have to work so hard to pump your blood throughout your body. But while blood pressure medications slow down your heart’s pumping action also depress the entire central nervous system. Or deplete electrolytes, in the case of diuretics which can translate into fatigue and other symptoms such as dizziness, weakness, or excessive urination.
Steroids
Corticosteroids, often called just steroids, are anti-inflammatory drugs. Most are synthetic forms of cortisone, a hormone naturally made in your adrenal glands. These include: prednisone, methylprednisolone, prednisolone, dexamethasone, and hydrocortisone.
Steroids don’t tend to cause significant side effects if they’re taken for a short time or at a low dose. Though sometimes they can cause some unpleasant side effects such as mood changes, increased appetite and difficulty sleeping.
Rapidly/abruptly stopping steroid medication however can lead to withdrawal symptoms, especially after extended use. Withdrawel symptoms that may occur are weakness, fatigue,nausea, vomiting, decreased appetite, weight loss, low blood sugar, dizziness, abdominal pain, diarrhea and menstrual changes.
5.Psychiatric (Mental Health)
Alcohol abuse
Alcohol abuse is a pattern of drinking too much alcohol too often. This can harm a person’s health, work and relationships. It can also lead to physical and psychological dependence. Fatigue experienced as a result of alcohol abuse may be linked to poor sleep quality (alcohol has been known to disrupt sleep) or permanent hangover symptoms.
Anxiety
Occasional anxiety is a normal part of life. People might feel anxious before giving a presentation, before making an important decision or when going through financial difficulty. However for some people, anxiety becomes so forceful, or frequent, that makes it hard to cope with daily life. Symptoms they experience include, irritability, muscle tension, difficulty controlling feelings of worry and feeling easily fatigued.
Depression
Sad, moody or feeling down, we are all familiar with these symptoms from time to time. But some people experience these feelings intensely and for long periods of time and it affects their life substantially. Depression can lead to a range of emotional and physical problems and can reduce a person’s ability to function at home and at work. Main symptoms of depression are: loss of interest or pleasure in daily activities, trouble sleeping, changes in appetite, loss of energy or increased fatigue, difficulty thinking or thoughts of suicide and death.
Drug abuse
Drug abuse, or substance abuse, is simply put the harmful or hazardous use of prescription and illegal drugs for non-medical reasons. It can result in harm to relationships, responsibilities and health. health, relationships, and responsibilities. Drug abuse can lead to physical dependence and addiction. Especially with stimulating drugs like cocaine and meth people sometimes experience intense exhaustion after using drugs. This crash is caused by the body’s attempts to balance out the over-stimulation of the central nervous system that occurred while a person was intoxicated.
Eating disorders (for example; anorexia; bulimia)
Eating disorders are serious conditions related to persistent eating behaviors that negatively impact your health, your emotions and your ability to function in important areas of life. The most common eating disorders are anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa and binge-eating disorder.
These eating disorders all show different signs and symptoms. But in general overeating can easily lead to fatigue, as the body uses all available energy stores to help with the digestion process. For people with anorexia or disordered eating habits, even a regular portion of food sometimes feels stressful to the body and will cause energy levels to drop.
Grief and bereavement
Losing a loved one is one of the most distressing experiences that people face. Most people experiencing grief and bereavement feel a variety of emotions like sadness, numbness, sorrow, loneliness and even anger and guilt. Some physical reactions to loss of a loved one include general tiredness or extreme fatigue at times, insomnia, loss of appetite, muscle weakness, anxiety attacks, suppressed immune system and increased blood pressure. Usually these feelings ease gradually and it will become possible for people to accept loss and to move forward.
6.Sleep Problems
Insomnia
Insomnia, or sleeplessness, is a sleep disorder where people have difficulty sleeping. They may either have difficulty falling asleep, or staying asleep as long as desired. Insomnia is typically followed by low energy, daytime sleepiness, irritability, and a depressed mood.
Narcolepsy
Narcolepsy is a lifelong disorder that affects the control of sleep and wakefulness. People with narcolepsy experience excessive daytime sleepiness and intermittent, uncontrollable episodes of sleep attacks. The exact cause of narcolepsy is unknown and there is unfortunately no cure.
Pregnancy
Fatigue is a common symptom during pregnancy. Some women may feel exhausted throughout their pregnancy and others may hardly feel tired at all. Fatigue during pregnancy is most common during the first trimester. The body is producing more blood to carry nutrients to the growing baby. Hormones, particularly an increase in progesterone levels are responsible for making the mother sleepy.
Fatigue usually goes go away during the second trimester, but often returns in the third trimester. At this point the mother is carrying extra weight from the baby and may experience difficulty sleeping.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
GERD happens when stomach acid moves up into the esophagus, the tube that connects the throat to the stomach. This backward flow is called reflux. The acid in the esophagus causes heartburn, possible tissue damage, nauseau, vomiting, bad breath and difficulty or pain when swallowing.
GERD can indirectly cause fatigue, because when you lie down and have an excess of stomach acid it can more easily wash back up into the esophagus than when your head is elevated (because of gravity). GERD then can affect your sleep because you may wait until the heartburn has passed before going to sleep, or you may experience discomfort while trying unsuccesfully to sleep.
Shift work or work shift changes
Irregular hours of work and work patterns like early morning and night shifts can disrupt the internal body clock and lead to sleep difficulties and fatigue.
Sleep apnea
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is an ailment where the upper passages of a person’s airway close off while they sleep. This deprives them of oxygen as the person stops breathing periodically throughout the night. Sleep apnea obviously ruins a good night’s sleep and leaves people feeling more exhausted than when they went to bed.
7.Vitamin Deficiencies
Folic acid deficiency
Folic acid (Vitamin B9) deficiency, or Folate deficiency, happens if the body does not get enough folic acid from a balanced diet. Vitamin B9 is one of many essential vitamins that is needed by the body for copying and synthesizing DNA, supporting nerve and immune functions and producing new cells. Symptoms of Folate deficiency include fatigue, irritability, diarrhea, smooth and tender tongue and poor growth. Folate is found in liver and grean leafy vegetables.
Iron deficiency
Iron deficiency is the most common nutritional deficiency in the world. Especially women of reproductive age (heavy periods and pregnancy) are at risk. The body needs iron to make a protein called hemoglobin. This protein helps red blood cells carry oxygen throughout the body’s tissues. So if there is not enough iron in the bloodstream the rest of the body cannot get the amount if oxygen it needs – and this results in anemia. Signs of iron deficiency include fatigue, difficulty maintaining body temperature, decreased immune function and an inflamed tongue.
Vitamin B12 deficiency
Vitamin B12, or cobalamin, is an important water-soluble vitamin. It is an essential vitamin for the human body to create red blood cells, nerves and DNA, and carry out vital functions while regulating the nervous system. Risk factors for a B12 deficiency include: following a strict vegan diet, old age, surgery that removes the part of the bowel that absorbs B12, not making enough stomach acid, the drug metformin for diabetes, long-term antacid drugs for heartburn.
Common symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency are weakness and fatigue. They occur because the body doesn’t have sufficient vitamin B12 to produce red blood cells, which transport oxygen throughout the body. This makes you feel tired and weak.

Vitamin D deficiency
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin that is created in the body when the skin is exposed to sunlight. It is present in only a small number of foods, like fatty fish, beef liver, egg yolks and fortified products, such as milk. People most likely to be affected by vitamin D deficiency are people with little exposure to sunlight. Some symptoms of a deficit in vitamin D include: exhaustion, muscle weakness, chronic pain, thinning or brittle bones, high or rising blood pressure, unexplained infertility.
8.Other
Cancer
Cancer is the abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. The use of tobacco is the cause of about 22% of cancer deaths. About 10% are the result of obesity, lack of physical activity, poor diet and excessive consumption of alcohol. Other factors are environmental pollutants, certain infections and exposure to ionizing radiation.
There are over 100 types of cancer so signs and symptoms depend on the type and grade of the cancer. Possible general signs and symptoms include a lump, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, prolonged cough, abnormal bleeding, and a change in bowel movements.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy uses anti-cancer drugs to slow or stop the growth of rapidly dividing cancers cells in the body. Even though chemotherapy targets cancer cells, also healthy cells may be damaged and can cause unpleasant side effects like fatigue, vomiting, nausea, hair loss and mouth sores.
Chronic fatigue syndrome
Chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS), or Myalgic Encephalitis (ME), is a long-term illness that causes extreme fatigue. The fatigue lasts for 6 months or more. People also report a combination of the following symptoms:
- Headaches
- Muscle pain
- Memory problems
- Tender lymph nodes
- Sleep problems
- Feeling unwell for more than 24 hours after physical activity
- Pain in multiple joints
- Sore throat
The cause for CFS is not yet understood, but potential triggers could be genes, mental health problems, hormone imbalances, bacterial/viral infections and problems with the immune system. While anyone can have it, it is most common in women in their 40s and 50s and it can last for years.
Fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia, or fibromyalgia syndrome, is a chronic condition characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain coupled with fatigue, sleep, memory and mood issues. The causes of fibromyalgia are still unknown but it probably involves a combination of:
- genetics (it tends to run in the family)
- infections (seem to trigger or aggravate fibromyalgia)
- physical or psychological trauma (stress can also be a trigger)
Normal muscle exertion
A feeling of tiredness or fatigue after exercise is a normal response to physical exertion. It is relieved by resting and there are a lot of people who even find the tiredness after exercise pleasurable. However, extreme or persistent fatigue after exercise could signal a health problem.
Obesity
Obesity is a complex disorder involving an excessive amount of body fat. It usually results from a combination of causes and contributing factors such as inactivity, unhealthy diet, genetics, family lifestyle, medical problems and certain medications. Obesity is diagnosed when your body mass index (BMI) is 30 or higher. Being overweight or obese isn’t just something cosmetic. It also increases your risk of health problems and diseases, such as high blood pressure, heart disease and diabetes.
Fatigue and your weight are also closely linked. When you are overweight your body simply has to work harder to engage in simple physical tasks, such as walking from the bus stop or climbing the stairs. A heavier body may also interfere with a good night’s sleep as it increases the chances that you suffer from sleep apnea.
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy uses targeted energy (radiation) to destroy cancer cells, shrink tumors, and/or reduce certain cancer-related symptoms. While radiation therapy is painless in itself, side effects occur as radiation therapy may also damage healthy cells and tissues close to the treatment area.
Since radiation therapy is a local treatment hairloss usually doesn’t occur unless the scalp is treated. Early side effects occur during or after therapy and are often gone within a few weeks after treatment. These include skin problems and feelings of fatigue. Late side effects occur months or years after treatment and often happen because of damage to blood vessels and connective tissue.
Rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic (long-term) autoimmune disease with an unknown cause that causes inflammation, stiffness, loss of mobility, pain, and erosion (deterioration) in the joints.
RA can affect almost any joint in the body, but initial symptoms typically affect the wrists, knuckles, balls of the feet, and/or knees. In addition to triggering painful joint swelling and stiffness over 90% of RA patients report fatigue as a symptom. It is counted second only to pain as the greatest challenge of living with RA.
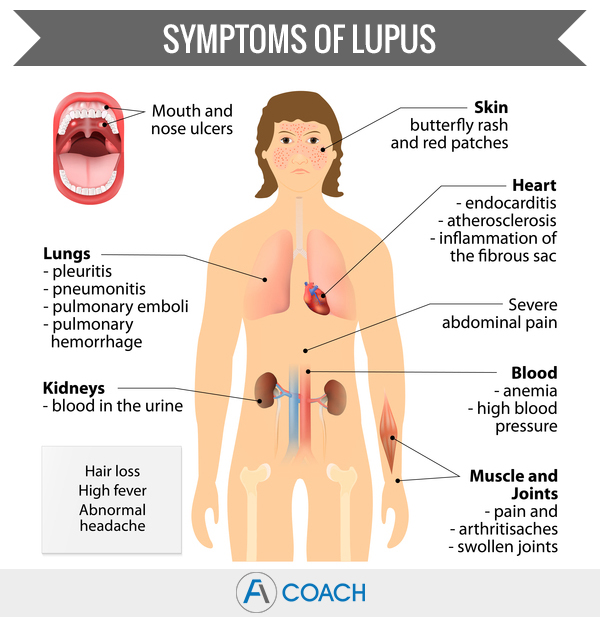
Systemic lupus
Also known as Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE), or just known as lupus, is a chronic inflammatory autoimmune disease in which the body attacks healthy cells and tissues, instead of bacteria and viruses. This may cause damage to many parts of the body like, skin, joints, kidneys, lungs, heart, blood vessels and brain. Common symptoms are fever, chest pain, panful and swollen joints, mouth ulcers, hair loss, feeling tired, swollen lymph nodes and a red rash typically on the face.
Often there are periods of illness (flares) and periods of wellness (remission) when there are not many symptoms.